Retinal Tears and Detachment
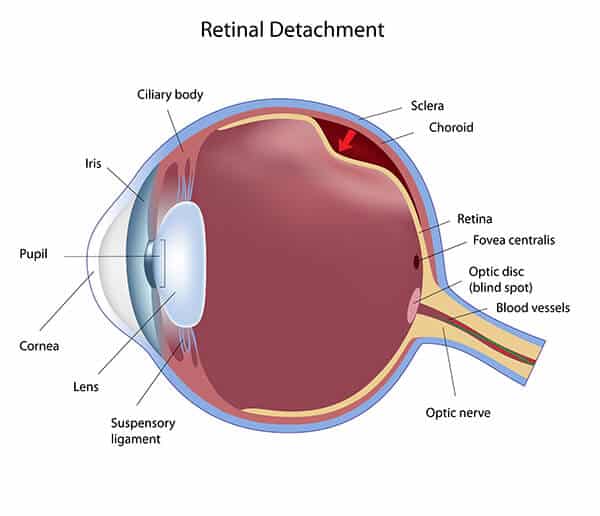
A sudden increase in floaters, with or without flashes, often indicates that the vitreous gel has separated from the back of the eye. This is known as a posterior vitreous separation, and occurs naturally, usually between the ages of 50 and 70. Most of the time when it does occur, no damage results, no treatment is required and the symptoms gradually subside over several weeks. However, in about ten percent of cases, it can lead to a tear in the retina which, if not treated, can then lead to a retinal detachment and serious permanent loss of vision. It is imperative that if a tear develops it is diagnosed and treated as soon as possible to prevent this from occurring. Retinal tears and detachments can affect anyone but are more common in nearsighted people, and those with a family history of the problem. If diagnosed early, a retinal tear can be treated in the doctor’s office with a laser or freezing treatment.
These are relatively quick and painless outpatient procedures that are effective in preventing the retina from detaching. If the tear is allowed to develop into a detachment, more serious surgery is required to repair it, often performed in a hospital operating room. This may involve surgically placing a scleral buckle, a device that resembles a small belt made of silicone material, which encircles the eyeball and is invisible from the exterior of the eye. Sometimes the gel is also removed from the eye in a procedure called a vitrectomy, and replaced with a bubble of gas which seals the tear in the retina and holds it in place while it is healing. Laser or freezing treatment is also used to glue the retina in place. If gas is used, the patient may be required to maintain a face-down position for up to several weeks and will be prohibited from flying in an airplane until the gas bubble disappears. In the best of circumstances, these procedures are effective in repairing the detachment in only 85 – 90% of cases, so it is much better to prevent the detachment through early diagnosis and treatment of the retinal tear.

